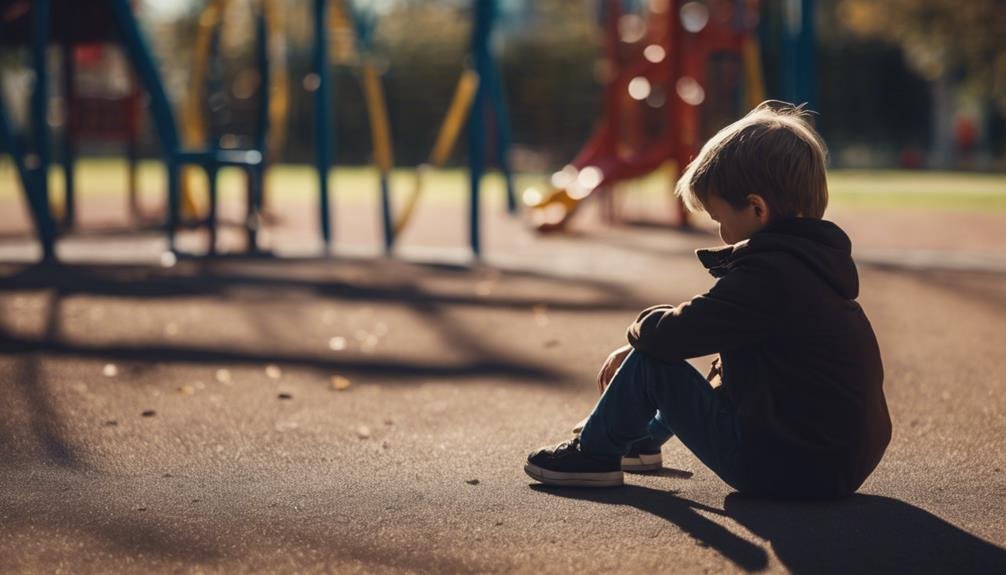
Domestic violence deeply impacts children’s behavior. They may struggle with regulating emotions, leading to mood swings and imitating violent behaviors. Witnessing violence instills fear, anxiety, and trust issues. Emotional scars can affect their well-being, resulting in struggles expressing emotions. Coping mechanisms develop, but emotional challenges require prompt recognition. The wounds may manifest in behaviors like aggression or withdrawal, carrying a heavy burden of guilt. Studies show a correlation to risky actions and substance abuse. Long-term behavioral issues can arise, affecting relationships and mental health. Understanding these effects is vital for promoting healing and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Witnessing domestic violence leads to externalizing behavior problems in children.
- Exposure instills fear, anxiety, and hypervigilance in children.
- Children may imitate violent behaviors they witness at home.
- Emotional scars from abuse profoundly affect children’s well-being.
- Trust issues and struggles in expressing emotions are common outcomes.
Behavioral Effects of Witnessing Violence
Witnessing domestic violence can have profound effects on children’s behavior, leading to a range of emotional and social challenges. Child Abuse and Exposure to violence at home can manifest in externalizing behavior problems such as aggression, defiance, and acting out in various environments. These children may struggle with regulating their emotions, resulting in mood swings and challenges in forming healthy relationships with peers and adults alike.
The Effects of Witnessing Domestic violence can also lead to children imitating violent or abusive behaviors they’ve observed, perpetuating a harmful cycle of violence into their own interactions. This exposure can instill fear, anxiety, and hypervigilance in children, impacting their overall well-being and sense of safety. Additionally, trust issues, attachment difficulties, and struggles in expressing emotions or needs are common outcomes for children who’ve experienced such trauma.
Understanding the Behavioral Effects of Witnessing Violence is important in addressing the long-term consequences it can have on children’s mental and physical health.
Impact on Emotional Well-being
When children witness domestic violence, the emotional scars left by the abuse can be profound, impacting their overall well-being.
Coping mechanisms are often developed as a way to navigate the complex emotions stemming from such traumatic experiences.
It’s essential to recognize and address these emotional challenges to prevent long-term psychological effects on children exposed to domestic violence.
Emotional Scars From Abuse
Children impacted by domestic violence often carry deep emotional scars that can profoundly affect their well-being and development. The emotional toll of abuse can lead to feelings of anxiety, fear, and struggles with regulating emotions.
Witnessing violence at a young age can result in long-term consequences such as low self-esteem, trust issues, and challenges forming healthy relationships. These emotional wounds may manifest in behaviors like aggression or withdrawal as coping mechanisms.
Children exposed to abuse may feel insecure, confused, and burdened with guilt or shame, impacting their self-perception. The trauma from domestic violence can leave lasting effects on a child’s emotional well-being, influencing their mental health and ability to navigate relationships.
It’s essential to recognize and address these emotional scars promptly to support children in healing and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
Coping Mechanisms Developed
Experiencing domestic violence can prompt children to develop coping mechanisms that impact their emotional well-being and overall mental health. The trauma of domestic violence can have profound effects on children, leading them to employ various coping strategies such as withdrawal, aggression, or substance abuse.
These coping mechanisms serve as a way for children to navigate the overwhelming emotional impact of witnessing violence in their homes. Signs of trauma, like fear, anger, or withdrawal, may indicate that children are utilizing coping mechanisms to cope with the distress caused by domestic violence.
Adolescents, in particular, may exhibit aggressive behavior or turn to substances as a means of managing their emotions in the face of ongoing violence. It’s essential for caregivers and professionals to recognize these coping mechanisms and provide the necessary support and interventions to help children heal from the emotional scars inflicted by domestic violence.
Guilt and Responsibility in Children

You may not realize it, but children exposed to domestic violence often carry a heavy burden of guilt and mistakenly believe they’re to blame for the abusive actions.
This sense of responsibility can create a deep well of internalized shame and self-blame within these children, affecting their emotional well-being and behaviors.
Understanding the significance of this false belief is vital in helping these children navigate the complex emotions tied to witnessing domestic violence.
Child Self-Blame Effects
In the aftermath of domestic violence, children often struggle with feelings of guilt and misplaced responsibility for the abuse they witnessed. The exposure to such violence can lead children to internalize blame, believing they caused or could have prevented the harmful situations.
This self-blame not only affects their mental health but also manifests in their behavior, leading to emotional distress, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Addressing children’s self-blame is vital for their healing and overall well-being. By providing support, reassurance, and guidance, caregivers and professionals can help mitigate the harmful effects of self-blame stemming from domestic violence exposure.
It’s crucial to validate children’s feelings, help them understand that the responsibility lies with the abuser, and empower them to process their emotions in healthy ways. By acknowledging and addressing child self-blame effects, we can support children in managing the complex aftermath of domestic violence and promote their emotional resilience and recovery.
Impact of Guilt
Children impacted by domestic violence often struggle with a profound sense of guilt and misplaced responsibility for the abusive situations they witness. Witnessing domestic violence can lead a child to internalize blame, believing they’re somehow at fault for the abuse they see. This burden of guilt can weigh heavily on their young shoulders, causing emotional distress, low self-esteem, and behavioral issues.
The child may feel overwhelmed by feelings of guilt, leading to anxiety and even depression as they work through the complexities of the abuse they witness. This misplaced sense of responsibility can hinder the child’s emotional development and impact their relationships with others. Addressing and alleviating the child’s feelings of guilt is essential for their healing and recovery from the trauma of domestic violence.
Responsibility Confusion Effects
How do responsibility confusion effects contribute to the emotional distress experienced by children witnessing domestic violence?
Children exposed to domestic violence often experience responsibility confusion effects, leading them to internalize feelings of guilt and shame. This internalized belief that they’re responsible for the abuse can result in heightened anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem in these children.
The conflicting emotions of love and fear towards the abuser further compound their sense of responsibility and confusion. As a result, children may struggle with understanding that they aren’t to blame for the violence they witness, perpetuating their emotional distress.
Addressing responsibility confusion effects is crucial in helping children affected by domestic violence recognize that the responsibility lies with the abuser, not with themselves. By providing support, reassurance, and counseling, we can help these children navigate their feelings of guilt and responsibility, ultimately aiding in their healing process.
Risky Behaviors and Substance Abuse
Studies consistently demonstrate a strong correlation between exposure to domestic violence and an increased likelihood of engaging in risky behaviors, particularly substance abuse, among affected children.
The trauma of witnessing violence can profoundly impact a child’s behavior, leading them to use substances as a coping mechanism for the emotional pain they experience. Research suggests that children who witness domestic violence are more prone to substance abuse issues in adolescence, potentially as a way to numb the distress caused by the violence they’ve witnessed.
This coping mechanism, while initially providing a sense of relief, can lead to more significant substance abuse problems later in life. It’s essential to understand that children exposed to domestic violence may turn to risky behaviors like substance abuse to navigate the trauma they’ve endured, highlighting the urgent need for support and intervention to break this cycle of harm and provide these vulnerable children with healthier coping mechanisms.
Signs of Teen Dating Violence

Adolescents are frequently impacted by dating violence, with one in three experiencing some form of abusive behavior. Recognizing the warning signs of teen dating violence is vital in supporting those affected. Changes in behavior, such as sudden mood swings or a decrease in social interactions, can indicate potential abuse. Physical signs like unexplained injuries or bruises shouldn’t be overlooked. Additionally, mental health issues and emotional trauma can result from teen dating violence, leading to long-term consequences.
Isolation from friends and family is a common red flag in abusive relationships. If you notice a friend or loved one becoming increasingly distant or secretive about their relationship, it’s imperative to offer support and create a safe space for them to share their experiences. Encouraging open communication and providing resources for help can make a significant difference in addressing teen dating violence.
Long-Term Consequences on Behavior
Children who witness domestic violence are at a pivotal risk of developing long-term behavioral issues that can greatly impact their social and emotional well-being. The effects of exposure to domestic violence on children’s behavior are profound and can lead to various long-term consequences.
Research indicates that children exposed to domestic violence may exhibit externalizing behaviors such as aggression, defiance, and conduct disorders. These behavior problems can manifest in emotional dysregulation, impulsivity, and challenges in forming healthy relationships. Additionally, persistent exposure to domestic violence can increase the likelihood of children developing antisocial behaviors, substance abuse issues, and engaging in criminal activities as they grow older.
The impact of domestic violence on children’s behavior extends into adolescence and adulthood, influencing their social interactions, coping mechanisms, and overall mental health. It’s important to address these long-term consequences early on to prevent further psychological problems and promote healing in children who’ve been exposed to domestic violence.
Addressing Trauma and Promoting Healing

Addressing trauma and promoting healing in children exposed to domestic violence is an important step towards mitigating the long-lasting impacts on their emotional and social well-being. Children who witness domestic violence may display trauma-related behaviors such as withdrawal, fear, and aggression, which can greatly affect their mental health.
It’s vital to recognize that exposure to violence can lead children to feel guilty and wrongly blame themselves for the abuse they witness, resulting in internalizing harmful emotions.
Trauma from domestic violence can manifest in various ways, including anxiety, excessive crying, and even aggressive behavior in children. Adolescents exposed to such violence are particularly vulnerable and may turn to substance abuse or exhibit signs of teen dating violence themselves.
Implementing safety planning for victims of domestic violence is essential not only to protect themselves but also to shield their children from harm during crisis situations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Violence Affects Children’s Development?
When violence impacts children’s development, emotional regulation, social interactions, academic performance, self-esteem, attachment styles, coping mechanisms, trust issues, mental health, aggression tendencies, communication skills, fear responses, and relationship patterns can be affected, leading to long-term consequences and the need for therapy options.
How Can Abuse Affect a Childs Behaviour?
You might notice that abuse can deeply affect a child’s behavioral patterns, emotional regulation, and trust issues. It influences social interactions, coping mechanisms, self-esteem, and academic performance, shaping their entire world.
What Are the Psychological Effects of Violence Against Children?
When violence is inflicted on children, they may experience a range of psychological effects such as trauma responses, difficulties with emotional regulation, attachment issues, trust issues, aggressive behavior, anxiety symptoms, and impacts on self-esteem.
Conclusion
As you navigate the intricate web of domestic violence’s impact on children, remember that each behavior is a brushstroke on the canvas of their lives.
These children carry the weight of what they’ve witnessed, shaping their actions and choices in ways unseen.
By recognizing these signs and addressing the trauma with compassion and support, we can help them paint a brighter future filled with healing and hope.